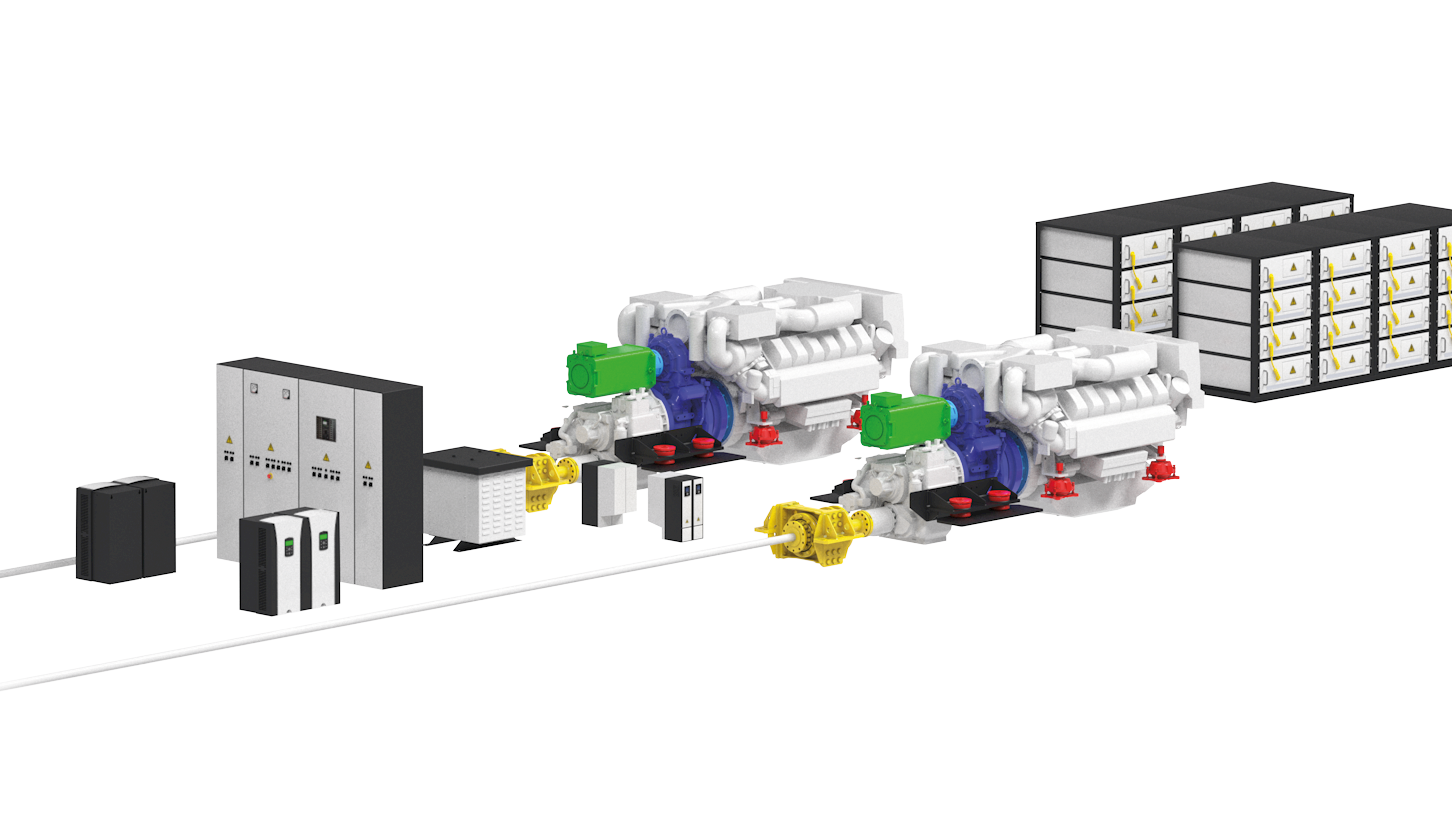
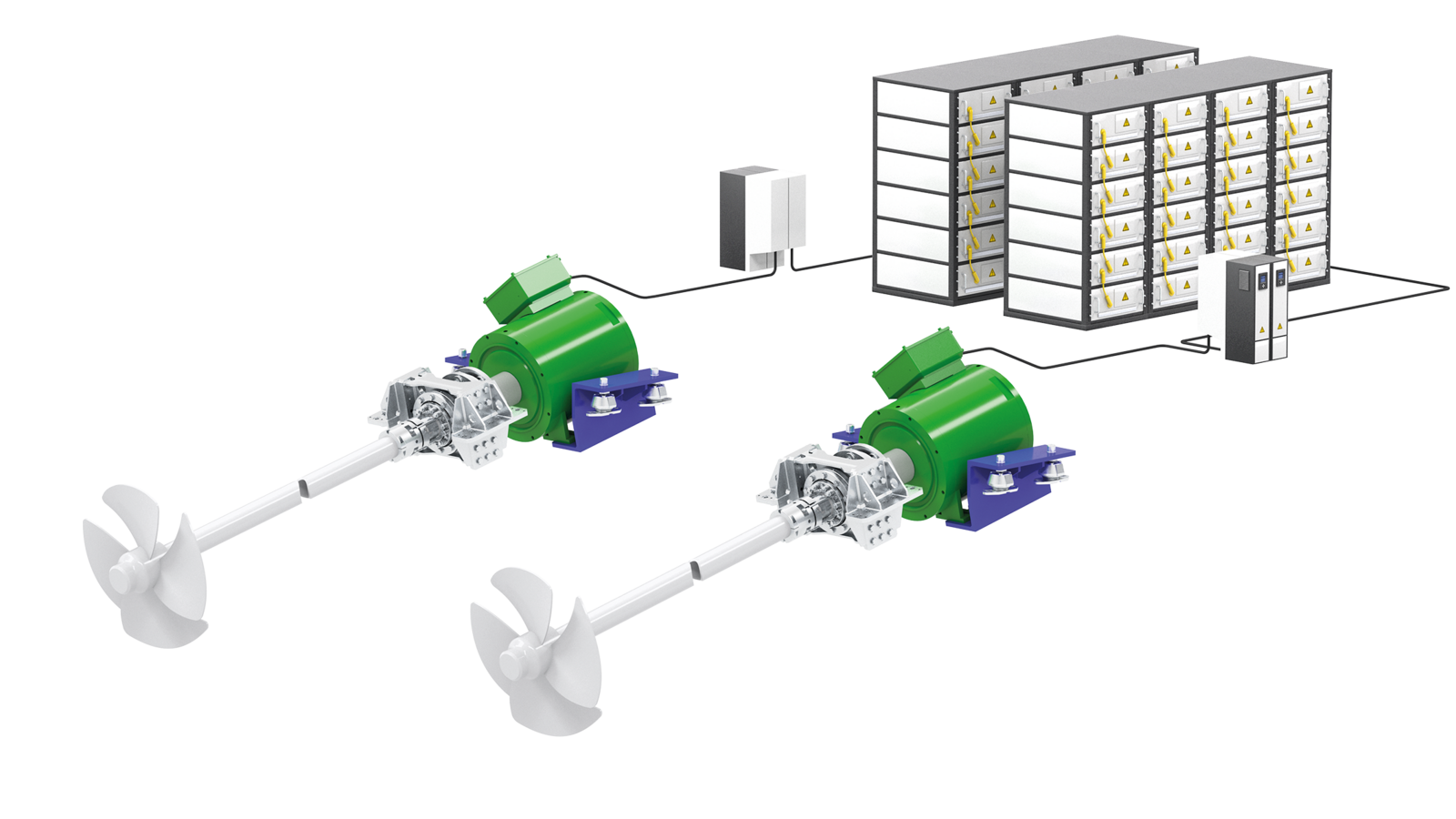
Types of Hybrid Drives
In order to decide which type of hybrid drive is suitable for the individual application and to find the best possible technological solution in terms of performance, design and efficiency, it is crucial to carry out a preliminary study and an analysis of the operating parameters. This is our team's favorite work.
There are basically two types of hybrid drives for all kind of vessels:
Advantages:
The first advantage of a serial hybrid propulsion system is offering significant flexibility to the propulsion system, optimizing the diesel engines’ performance, improving their efficiency. This flexibility is due to the complete separation between energy sources and users, allowing for more efficient energy management. Providing greater independence to the primary power source, the diesel engine, mechanically decoupling it from the propulsion line, also contributes to a higher level of comfort on board, significantly reducing noise and vibrations.
Disadvantages:
However, adopting this type of propulsion has a considerable impact on the overall vessel cost: The more complex the system, the higher the level of design required to make it as complete and efficient as possible, and in line with the vessel‘s needs and requirements. The initial investment will thus be higher compared to traditional propulsion. On the other hand, retrofitting a traditional propulsion with a hybrid one is a brilliant example of applying circular economy principles, reusing everything possible already installed on board, integrating it into the new design, thus is reducing the environmental impact and making it even more sustainable.
Advantages:
Compactness and lightness are perfect for limited spaces, the robustness and reliability of the system ensure consistent performance over time. Thanks to modularity, obtained through the standardization of hybrid components, and advanced electrical design safety, compliant with the highest industrial standards, an additional safety level is added. Customization allows for tailor-made solutions, combining diesel engines of various powers with electric motors suitable for the specific needs of the project and customer; package‘s flexibility makes it ideal for both, pleasure and commercial vessels.
Disadvantages:
On the other hand, the parallel configuration (with “secondary shaft”) is characterized by greater flexibility in managing the reduction ratio between the electric machine and the propeller shaft, optimizing the propulsion system‘s efficiency. Such a configuration will consequently have a greater overall weight, due to the use of an additional mechanical transmission, as well as an electric motor. This affects both, the vessel‘s fuel consumption and requires more installation space. Parallel hybrid is the most common choice for medium-small units, where the available space is limited, annual operating hours rarely reach high values (5,000 hours), and comfort and relaxation are the user’s priorities.